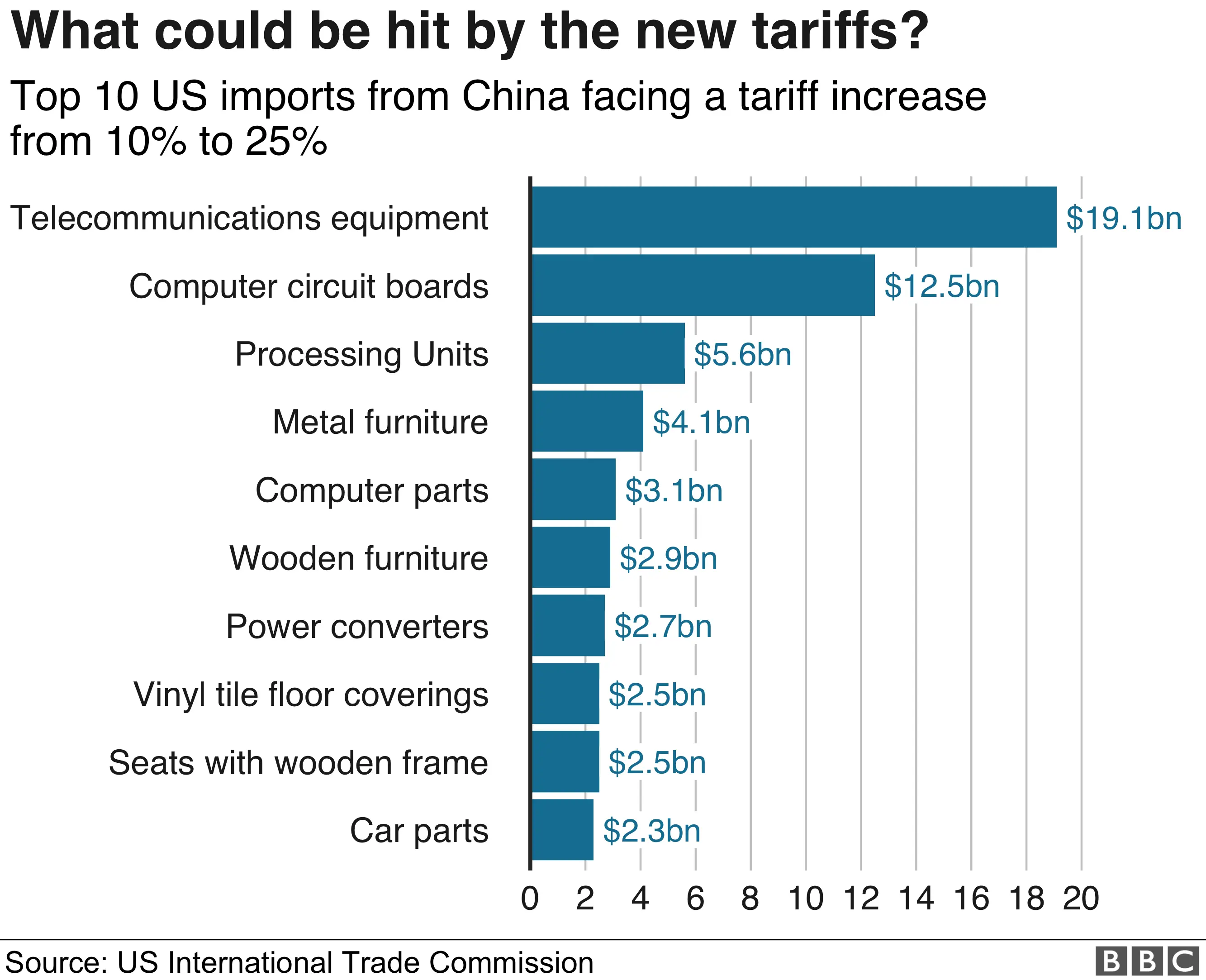
Understanding the US-China Trade War and Its Global Impact
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The US-China Trade War has reshaped global commerce and impacted the global economy.
- Originating in 2018, it involves mutual tariffs and trade restrictions due to perceived unfair practices.
- Consumers face higher prices and reduced choices; industries suffer losses, and jobs are affected.
- Companies are adapting by shifting supply chains and implementing new strategies.
- The conflict has led to strategic economic decoupling and technology restrictions.
- Global trade patterns are changing, affecting emerging markets and international institutions.
- The future remains uncertain, with ongoing political dynamics influencing the outcome.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the US-China Trade War and Its Global Impact
- What is a Trade War?
- Origins and Escalation: How Did We Get Here?
- Economic Impact: Counting the Cost
- Supply Chain Shifts: Adapting to New Realities
- Strategic Economic Decoupling
- Global Trade Implications
- Political Dynamics and Future Outlook
- Looking Ahead: What’s Next?
- Frequently Asked Questions
The trade war between the United States and China stands as one of the most significant economic conflicts of our time. This battle between the world’s largest economies has reshaped global commerce, affecting everything from consumer prices to international supply chains. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore how this trade war has transformed the global economic landscape and what it means for businesses and consumers worldwide.
What is a Trade War?
A trade war occurs when countries impose tariffs and trade restrictions on each other in response to perceived unfair economic practices. The US-China trade war, which began in 2018, represents an unprecedented escalation in economic tensions between these global powerhouses, with far-reaching consequences for international trade and growth.
Origins and Escalation: How Did We Get Here?
Historical Context
The roots of this conflict trace back to China’s entry into the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001. Over the following years, several key issues emerged:
- A massive trade deficit reaching $375 billion by 2017
- Limited market access for US companies in China
- Forced technology transfers
- Allegations of intellectual property theft
Trigger Events
The conflict officially began in 2018 when the US imposed tariffs on $50 billion worth of Chinese goods, including:
- Steel
- Solar panels
- Various manufactured goods
China quickly retaliated with duties on:
- US soybeans
- Automobiles
- Other key exports
By 2019, the dispute had escalated dramatically, with US tariffs affecting $350 billion in Chinese goods and Chinese retaliatory duties impacting $100 billion in US products.
Economic Impact: Counting the Cost
Consumer Impact
The trade war’s effects on consumers have been substantial:
- Monthly cost to US consumers: $1.4 billion
- Reduced product choices
- Higher prices across multiple sectors
Industry Losses
Several sectors have faced significant challenges:
- US manufacturing hit by reduced exports
- Agricultural exports to China dropped 75%
- Chinese tech firms struggled under US export controls
Employment and Growth
The broader economic impact includes:
- 300,000 US jobs lost
- 0.3% reduction in real GDP
- Significant financial market volatility
Supply Chain Shifts: Adapting to New Realities
Companies have responded to the trade war by:
- Relocating production to countries like Vietnam and Mexico
- Implementing dual sourcing strategies
- Increasing automation to reduce tariff exposure
Notable changes include:
- Vietnam’s foreign direct investment surge of 7% in 2020
- Major companies like Apple diversifying their manufacturing bases
- Development of new regional supply hubs
Strategic Economic Decoupling
Technology Restrictions
The conflict has led to significant tech sector changes:
- US bans on companies like Huawei
- Stricter semiconductor export controls
- Increased scrutiny of Chinese tech investments
Investment Changes
New barriers have emerged in:
- Critical sectors (AI, biotech)
- Cross-border acquisitions
- Research collaboration
Global Trade Implications
The ripple effects have been felt worldwide:
Emerging Markets
- Short-term gains for countries like Mexico and Vietnam
- Infrastructure challenges in beneficiary nations
- Shifting trade patterns globally
Trade Pattern Changes
- EU becoming China’s largest trading partner
- Reduced US-China bilateral trade
- Formation of new trading relationships
WTO Impact
- Multiple disputes filed
- Weakened multilateral trading system
- Reduced faith in global trade governance
Political Dynamics and Future Outlook
Domestic Pressures
Both countries face internal challenges:
- US manufacturers and farmers seeking tariff relief
- Chinese push for technological self-reliance
- Strong public opinion influencing policy decisions
Resolution Prospects
The path forward remains complex:
- Limited progress on structural issues
- Ongoing bilateral negotiations
- Shift toward broader strategic competition
Looking Ahead: What’s Next?
The trade war has permanently altered the global economic landscape. Key takeaways include:
- Higher costs for consumers and businesses
- Fragmented supply chains
- Weakened international trade institutions
- Ongoing economic decoupling
Recommendations for Businesses:
- Diversify supply chains
- Monitor policy changes closely
- Invest in automation and efficiency
- Build regional partnerships
- Develop contingency plans
The US-China trade war represents more than just a temporary dispute—it’s a fundamental shift in global economic relations. As businesses and nations continue to adapt, the importance of resilient strategies and diversified approaches becomes increasingly clear.
Frequently Asked Questions
What caused the US-China trade war?
The trade war was initiated due to the US government’s concerns over China’s trade practices, including a significant trade deficit, limited market access, forced technology transfers, and allegations of intellectual property theft.
How has the trade war affected consumers?
Consumers have faced higher prices on various goods, reduced product choices, and an overall monthly cost increase estimated at $1.4 billion due to the imposed tariffs.
What are the long-term global implications?
The trade war has led to fragmented supply chains, shifts in global trade patterns, weakened international trade institutions, and a move toward economic decoupling between the US and China.
How are businesses adapting to the trade war?
Businesses are diversifying their supply chains, investing in automation, building regional partnerships, and developing contingency plans to mitigate the impact of tariffs and trade restrictions.
Is there a resolution in sight for the trade war?
While negotiations continue, progress on structural issues remains limited. The situation is complex, with ongoing strategic competition influencing the prospects for a comprehensive resolution.
2 thoughts on “Understanding the US-China Trade War and Its Global Impact”
Comments are closed.